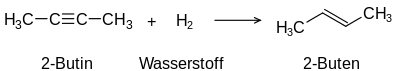Utente:Grasso Luigi/sanbox1/Composti saturi e insaturi
In chimica organica, un composto saturo è un composto chimico con un legame singolo. Mentre se possiede legami doppi o tripli viene detto composto insaturo.
Composti saturi[modifica | modifica wikitesto]
| Composti saturi | |
| Etano | Propano |

|

|
| 1-Ottanolo | |
| Acidi grassi saturi | |

| |
I composti saturi possiedono unicamente singoli legami carbonio-carbonio.
Proprietà[modifica | modifica wikitesto]
I composti saturi sono generalmente più stabili e meno reattivi dei composti insaturi poiché non hanno impedimenti sterici e nemmeno notevoli differenze di polarità. Inoltre, hanno punti di fusione e di ebollizione bassi in confronto alla massa molare.
Esempi[modifica | modifica wikitesto]
Idrocarburi saturi[modifica | modifica wikitesto]
Alcooli, aldeidi, chetoni, acidi carbossilici ed esteri[modifica | modifica wikitesto]
- Butanolo, acetaldeide, propanone, acido butirrico
- Acidi grassi saturi (e.g., acido stearico e acido palmitico)
Composti insaturi[modifica | modifica wikitesto]
| Composti insaturi | ||
| Etene | Etino | |

|
||
| Acido linoleico | ||

|
||
I composti insaturi sono composti organici la cui struttura molecolare contiene uno o più doppi o tripli legami carbonio-carbonio. Questi possono anche essere coniugati. Esempi sono gli acidi grassi insaturi o gli idrocarburi insaturi (alcheni e alchini). Molte sostanze naturali sono composti insaturi.
Storia[modifica | modifica wikitesto]
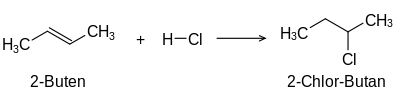
The term unsaturated compounds, originally unsaturated hydrocarbons, derives from their ability to carry out typical addition reactions which are not possible with saturated compounds such as alkanes:
Addition of hydrogen to an alkyne
Addition of hydrogen chloride (chlorination)
Here, the only formally unsaturated aromatics differ from the other unsaturated compounds: due to the high stability of the aromatic system, aromatics do not carry out the typical addition reactions or only under extreme conditions such as high temperature or high pressure. Instead, substitution reactions are preferred.
Proprietà[modifica | modifica wikitesto]
Unsaturated compounds are generally more reactive than saturated compounds. Triglycerides (rapeseed oil, linseed oil, olive oil, etc.) with a high content of unsaturated fatty acid residues turn more rapidly rancid than those with a high proportion of saturated fatty acid residues ,as for example coconut fat.
In a long chain of carbons, such as a fatty acid, a double or triple bond will cause a kink in the chain. These kinks have macro-structural implications. Unsaturated fats tend to be liquid at room temperature, rather than solid, as the kinks in the chain prevent the molecules from packing closely together to form a solid. These fats are called oils and are present in fish and plants.
In other unsaturated hydrocarbons, the double bond between two carbons prevents rotation of the atoms about the bond, locking them into specific structural formations. When attached atoms occupy similar positions on each carbon, they are referred to as "cis", and when they are on opposite sides, they are called "trans". Most natural hydrocarbons exist in the cis state, but artificially manufactured hydrocarbons are trans. The body lacks the enzymes to properly break down the trans configuration. This is why trans fats are viewed as dangerous and unhealthy, as they tend to build up. Unsaturated compounds of the two formations are classified as geometric isomers of one another.
The amount of unsaturation of a fatty acid can be determined by finding its iodine number.
Esempi[modifica | modifica wikitesto]
Idrocarburi insaturi[modifica | modifica wikitesto]
Alcooli, aldeidi, chetoni, acidi carbossilici ed esteri[modifica | modifica wikitesto]
- Ascorbic acid, acetylformoin, bombycol, retinol
- Citronellal, crotonaldehyde, E160e, furfural, retinal, saffronal
- Abscisic acid, anthrone, cyclohexenone
(the solution which contains as much solute as it can dissolveat thesaid temperature in the presence of undissolved solute particles is called a "SATURATED SOLUTION")
Note[modifica | modifica wikitesto]
Voci correlate[modifica | modifica wikitesto]