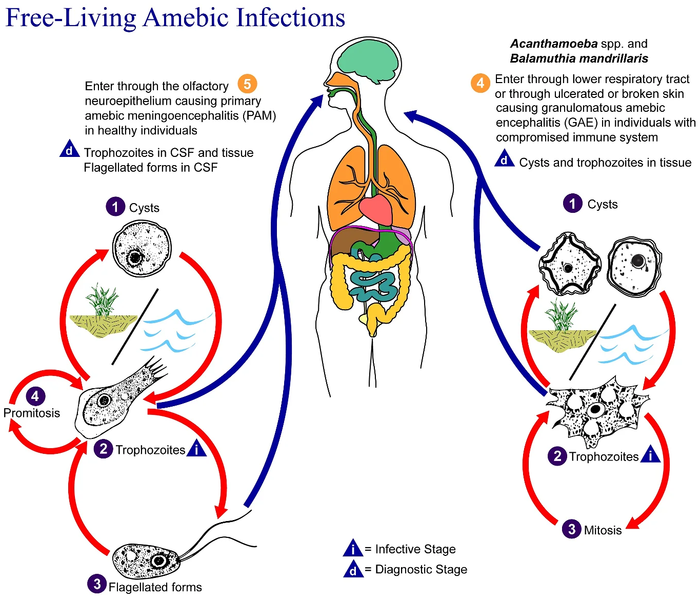
File:Free-living amebic infections.png
Vai alla navigazione
Vai alla ricerca
Dimensioni di questa anteprima: 700 × 600 pixel. Altre risoluzioni: 280 × 240 pixel | 560 × 480 pixel | 896 × 768 pixel | 1 195 × 1 024 pixel | 1 365 × 1 170 pixel.
File originale (1 365 × 1 170 pixel, dimensione del file: 715 KB, tipo MIME: image/png)
Cronologia del file
Fare clic su un gruppo data/ora per vedere il file come si presentava nel momento indicato.
| Data/Ora | Miniatura | Dimensioni | Utente | Commento | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| attuale | 11:24, 2 feb 2023 |  | 1 365 × 1 170 (715 KB) | Materialscientist | https://answersingenesis.org/biology/microbiology/the-genesis-of-brain-eating-amoeba/ |
| 08:30, 20 lug 2008 |  | 518 × 435 (31 KB) | Optigan13 | {{Information |Description={{en|This is an illustration of the life cycle of the parasitic agents responsible for causing “free-living” amebic infections. For a complete description of the life cycle of these parasites, select the link below the image |
Pagine che usano questo file
La seguente pagina usa questo file:
Utilizzo globale del file
Anche i seguenti wiki usano questo file:
- Usato nelle seguenti pagine di de.wikibooks.org:
- Usato nelle seguenti pagine di en.wiktionary.org:
- Usato nelle seguenti pagine di fi.wikipedia.org:
- Usato nelle seguenti pagine di fr.wikipedia.org:
- Usato nelle seguenti pagine di gl.wikipedia.org:
- Usato nelle seguenti pagine di hr.wikipedia.org:
- Usato nelle seguenti pagine di is.wikipedia.org:
- Usato nelle seguenti pagine di pl.wikipedia.org:
- Usato nelle seguenti pagine di te.wikipedia.org:
- Usato nelle seguenti pagine di vi.wikipedia.org:
- Usato nelle seguenti pagine di www.wikidata.org:
- Usato nelle seguenti pagine di zh.wikipedia.org: